What Are Volleyball Shoes

Identification and recognition of volleyball shoes among the abundance of other sports shoes is not as easy as understood. Though they may appear similar to other athletic shoes, their design, anatomy, types, and fit criteria are quite different.
Volleyball shoes are specifically designed for the sport, with features that cater to the unique demands of volleyball. They typically have a gum rubber sole for excellent traction, a cushioned midsole and uppers to improve bounce, and other essential components.
Whether you are buying your first pair of volleyball shoes as a newcomer or replacing a well-worn pair as a seasoned athlete, you must learn what are volleyball shoes and how they differ from other sports shoes.
So, If you don’t know, keep reading, as in this beginner’s guide, we will discuss the key parts, types, materials they are made from, anatomy, and other essential information about volleyball shoes.
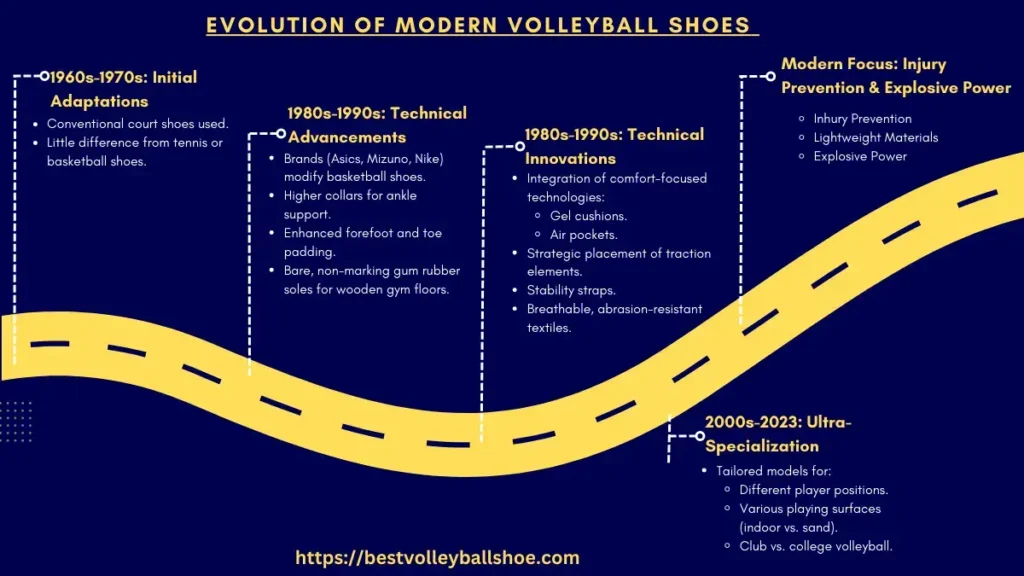
Evolution/History of Modern Volleyball Shoes
Volleyball shoes have come a long way from their early beginnings as essential chuck-style basketball sneakers. Through ongoing innovation in materials and design, they now represent highly specialized athletic performance footwear.
What Are Volleyball Shoes Made Of?
Volleyball shoes are constructed from specialized materials to provide the ideal combination of traction, support, and lightness on the court. To gain a better understanding of what makes the construction of volleyball footwear unique, let’s explore some of the critical materials these athletic shoes are typically made from.
Non-marking gum rubber
The outsoles of volleyball shoes use non-marking gum rubber. This specialized rubber provides excellent traction on indoor court floors without scuffing or leaving behind marks.
EVA (ethylene vinyl acetate) foam
It is commonly used to make the midsole of volleyball shoes. This lightweight foam offers cushioning and shock absorption to cushion the feet during repetitive landings while jumping. Some midsoles also incorporate TPU (thermoplastic polyurethane) in high-impact areas.
Synthetic leather
Synthetic leather overlays provide structure and support. Mesh fabric sections add ventilation to allow airflow, preventing heat and moisture build-up inside the shoe during intense play. This blend resists abrasion while retaining breathability.
Thermoplastic Polyurethane (TPU)
Extra layers of TPU are positioned in high-wear areas prone to impact and abrasion, like the toe box and along the ankle collar. This protects the feet during slides, digs, and dives.
Adhesives
Advanced bonding adhesives combine all the layers and pieces together. This adhesive withstands the demands of aggressive volleyball movements over time without layers separating.
Anatomy and Parts of Volleyball Shoes
Volleyball shoes contain several defining features that differentiate them from conventional athletic shoes and make them optimized for the demands of volleyball.
Uppers
Uppers use durable synthetic leather and breathable mesh fabrics to provide structure while allowing ventilation during active play. The materials resist abrasion from diving and extend high enough to support ankles fully.
Midsoles
Sandwiched between the outsole and upper, volleyball shoe midsoles are lightweight to allow freedom of movement. However, they still incorporate ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) foam or similar shock-absorbing materials. Some also have a contoured shape for arch support.
Outsoles
The outsoles of volleyball shoes are designed to provide solid traction on hard indoor courts, allowing players to start and stop rapidly while reducing sliding.
They incorporate grip patterns with quality, durable rubber to maintain traction. The midsole and outsole also provide cushioning from impacts.
Ankle Support
Many volleyball shoes are high-tops, with collars padded and reinforced to lend ankle stability and help prevent dangerous rolls and sprains. Some are lower-cut for those wanting more freedom.
Toe Box
Shoes made for volleyball have an extra durable toe box to withstand the drag of toe-diving spikes. Padding reduces injury when landing incorrectly.
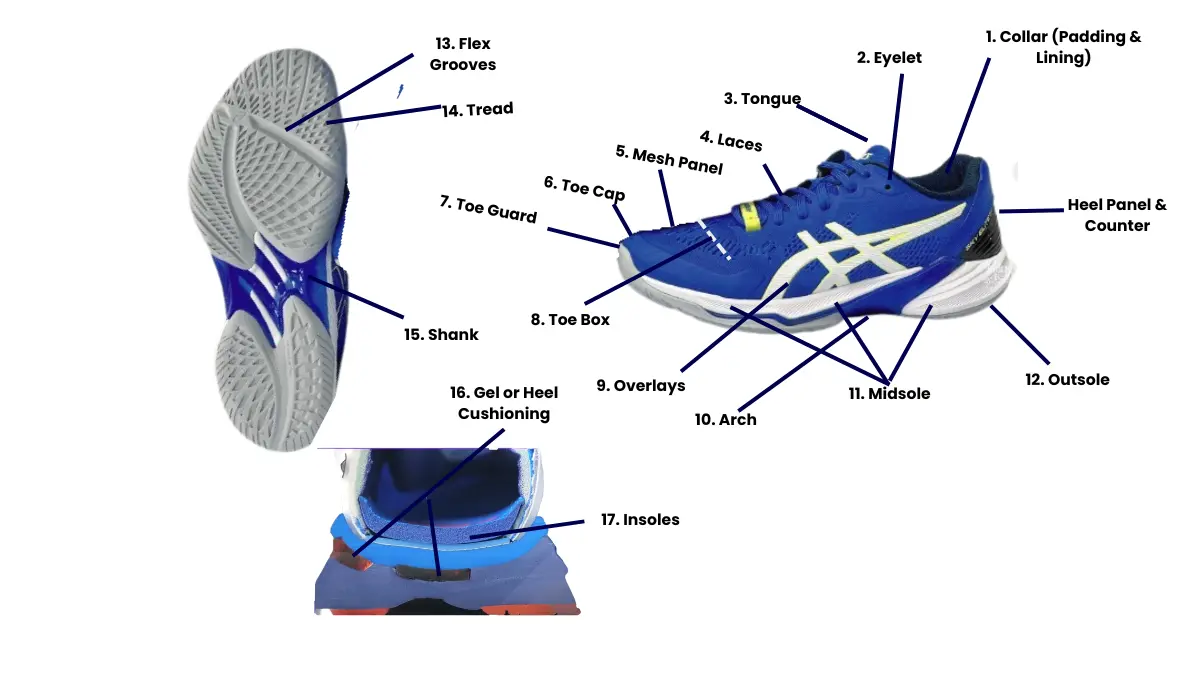

The different parts of volleyball shoes in the upper include:-
- Collar: Adequately padded for ankle support, comfort and decent fit
- Eyelets: The hole in the upper for the passage of laces. Mostly these holes contain circuit rivets of metal or plastic to prevent them from ripping due to laces
- Tongue: A piece usually made of mesh, placed Underneath the laces to cover the forefoot and protect it from being rubbed by the laces. May be separate from the shoe upper or in a booty or sock-like construction as a one-piece upper.
- Laces: Also known as shoelaces or shoe strings. Mainly there for tightening and protecting the foot inside the shoe and also for keeping the shoe intact and preventing it from flying away while playing.
- Mesh-made panel:– For adequate breathing and to keep the foot cool and dry during intense and long games.
- Toe Cap: A small piece of material mainly used for reinforcement.
- Toe Guard: Made of a dura shield to withstand the drag of toe-diving spikes and prevent injuries.
- Toe Box: The front area of the shoe protects the front foot It is Usually padded and has a breathable construction.
- Overlays: These are leather-made materials for keeping the foot in shape and adding stability and durability.
- Arch: The center of the shoes with shaped like an arch. Mostly, varies for flat and normal feet i.e. flat-foot athletes use low-arch shoes whereas athletes with normal feet have a comparatively high arch.
- Midsole: Usually for providing a smooth comfy landing after spike.
- Outsole: Made of nonmarking rubber to provide excellent traction on the court.
- Flex Grooves: For enhancing flexibility and allowing more natural movements.
- Tread: Made of rubber for providing excellent traction and gluing with the surface. These have similar jobs to the treads in the car types. Also an indicator of shoe life and performance.
- Shank: It is made of a rigid material (plastic or metal). Place between the outer and inner soles to provide support and stability.
- Heel Cushioning: Gel pockets or any cushioning material for making the landing comfortable for the heel and preventing impact after jumps.
- Insoles: These may be glued or removable. Provide comfort, smoothness, and support to the foot.
Types of Volleyball Shoes
There are a few critical ways that volleyball shoes can be categorized based on their design and intended use:
Indoor Versus Outdoor Volleyball Shoes
Most volleyball is played indoors, so shoes made for the hard court surface feature non-marking gum rubber outsoles, providing solid traction but without scuffing floors. Outdoor volleyball shoes have durable rubber treads better suited to grip grass or sand courts.
Position-Specific Volleyball Shoes
Some volleyball shoes cater to the needs of certain positions:
Major Brands
Most major athletic brands like Nike, Adidas, Mizuno, and Asics produce volleyball shoes with lightweight uppers, good traction, and ankle support to aid quick movement and jumping.
Special volleyball brands like Under Armour, Dreamees, and Nfinity also engineer shoes with extra padding, flexibility, and stability in critical areas that volleyball players need for positional play.
What to Look For When Selecting Volleyball Shoes?
With an understanding of the designed purpose and available types of volleyball shoes, players can evaluate and select the ideal volleyball footwear for their individual needs by considering these key factors:
Court Type
It determines whether you need a sole designed for indoor or outdoor play. If you mainly play indoors, choose a tread pattern suitable for indoor courts to avoid quick wear from outdoors.
Playing Position & Game Style
If you play volleyball, consider your position and playing style. Different positions require specific features: Setters benefit from flexibility. Hitters prefer a lightweight feel. Liberos may need extra padding.
Fit & Size
It’s vital to get accurately fitted shoes accounting for the width, arch type, and dimensions of your feet. Well-fitted shoes significantly impact comfort and safety.
Ventilation Zone
Ensure proper airflow to your feet during intense play by searching for volleyball shoes with mesh fabric panels. This feature helps maintain breathability, preventing discomfort and allowing you to easily focus on the game.
Ankle Support Level
For players with weak ankles or those engaged in straight-on hitting/blocking, consider opting for more rigid, high-top shoes. Alternatively, lower shoes sacrifice some support in exchange for increased mobility. If you want additional details when choosing volleyball shoes [Read more: How to choose volleyball shoes]
Care and Maintenance of Volleyball Shoes
Making volleyball shoes last longer while preserving their performance requires following some primary care and maintenance:
Cleaning: Use mild dish soap and water with a small brush to regularly clean the soles and uppers, removing dirt and sweat residue that can break down materials over time.
Storage: Let shoes fully air dry after games or practices before storing. Stuff with paper or shoe trees to hold the shape. Store in breathable mesh bags, not airtight plastic.
Inspect Wear: Check areas like the toe box treads. Mesh fabric for tearing or excessive abrasion. Replace shoes once they lose structural integrity or traction.
Replacement Guideline: On average, indoor volleyball shoes should be replaced after 50-60 hours of playtime as cushioning and traction degrade through use.
Taking five extra minutes to clean and inspect volleyball shoes after intense use can nearly double their lifespan, so if you want thorough guidelines for the maintenance of your volleyball shoes, read details in my article on how to clean volleyball shoes?
Wrapping it Up
Last of all, volleyball shoes are a vital piece of gear engineered explicitly for the fast-paced, explosive sport of volleyball.
What are volleyball shoes? From their grippy non-marking soles to breathable abrasion-resistant uppers and advanced midsole cushioning systems, every component aims to enable rapid bursts of sprints, jumps, and dives integral to excelling at volleyball.
Understanding volleyball shoe classifications, primary features, selection criteria, care, and the ongoing evolution of the footwear gives players the confidence they’re choosing the right shoe.
This allows them to avoid injury, eliminate shoe-related hindrances, and unlock their best possible play through technology genuinely optimized for the demands of the volleyball court.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why are volleyball shoes different from other court shoes?
Volleyball shoes differ by having a gum rubber outsole for indoor courts, a reinforced toe box for diving, and more padding and support for jumps and quick lateral movements. They optimize the traction and stability needed in volleyball.
What is the difference between indoor and outdoor volleyball shoes?
Indoor shoes have soles with solid rubber, providing grip without marking floors. Outdoor shoes have durable treads for grass and sand. The uppers also differ with more mesh for breathability outdoors.
What are the key things to look for in volleyball shoes?
Consider the fit, court surface, cushioning, ankle support level and height, toe protection, breathability/ventilation, and outsole traction patterns when selecting volleyball shoes.
Can you wear volleyball shoes casually?
While designed for performance, some volleyball shoes work fine casually. Usually, the lower or mid-cut models apply the cushioning and support features to casual use. Higher models look more athletic.
How long should volleyball shoes last?
With consistent play, indoor volleyball shoes should be replaced every 50-60 hours of court time as the cushioning and traction degrade through use over time after breaking in.





